# Account Protocol
TOP AI Network uses an account model. The account is the basis of all the TOP AI Network's activities.
The address is the unique identifier of an account, and a private key signature is required to operate an account.
# Account Object
An account is an object that contains state information and logic, which includes balances, properties of stored data, and actions for each property.
The account property is an object of user-defined data that is added as a key-value pair, and the user balance is a special property.
A key is an arbitrary String whose value can be any data type, such as integer, String, list, HashMap, and so on.
An action can be a system-level function, such as transfer or a custom action managed by the application smart contract deployed by the account owner.
Account objects and their methods can be easily and flexibly extended with new properties and custom actions
# Account Address
# Account Address Type
The account address types are shown in the table below.
| Account Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal User Account | Independent Account: T8000. |
| Application Smart Contract Account | T30000, sub account of the independent account.Is created when the contract is deployed. |
| System Smart Contract Account | Beacon System Smart Contract Account:T20001 or T20002; Shard System Smart Contract Account:T20000. |
Example:
Independent Account: T800002276a7d58218ac4978733e5cca927a7d86cb7c87
Shard System Smart Contract Account: T20000ML7oBZbitBCcXhrJwqBhha2MUimd6SM9Z6
# Special Account Address
| Account address | Description |
|---|---|
| T!0001Ebj8hBvoLdvcEEUwNZ423zM3Kh9d4nL1Ug | Destruction address, used to destroy governance rewards, zero workload rewards, etc. |
# Account Address Format
TOP address encoding format:
| 0 | 1 | (2,6) | n | @ | subaddr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | Account type | ledger id | Public key address | @ | suffix |
| Format | Length | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Prefix Identification | 1 byte | T: Means TOP. |
| Address Type (addr_type) | 1 btye | !: Destruction account 0 or 8: Normal account 2: Shard system contract account 3: User contract account 21 or 22: Beacon system contract account a: Table block account |
| ledger_id | 4 Hex characters | Consists of "0" (chain-id of main chain) and zone-index. zone-index:
|
| public address | - | Base58 encoding of the public key Hash. |
| sub_address | - | Optional, the table to which the account belongs. For example, the Beacon system contract account is "T-21-38NN9R9DoXrEhaEGKjGDzSmY1ZfgLqSetvQ@0", where "@0" means that the system account is in table 0 in the Beacon network. This data can print the account to the corresponding network segment. |
# Account Address Verification Rules
Position [0] must be "T".
Position [1] needs to be one of the account types.
Position [2-6] is a 4-digit special string:
ledger_id needs to be converted from hex to uint32.
ledger_id (uint32) contains the account version information.
ledger_id algorithm:
const std::String Text_ledger_id = account_addr.substr(2,4);//always 4 hex chars ledger_id = (uint16_t)xText_utl::hex2uint64(Text_ledger_id);Get the account version from ledger_id:
uint32_t version = (((uint32_t)ledger_id) << 8) | ((uint32_t)addr_type);
Position [7-end] is the public key address.
Definition of end:
- If there is no'@', "end" is the end.
- If there is '@', then '@'-1 is the end.
Public key address verification:
Public key address:
public_address = substr(account, 6, end) // Starts from position 6 to the endThe public key address pushes back the public key information, if ecdsa can unlock the public key.
ecdsa_address_decode(public_address.c_str(), version, HASHER_SHA2D, out) == 1;
# Account Space Shard Mapping
The process of account space mapping to sharding is as follows:
Beacon System Smart Contract Account
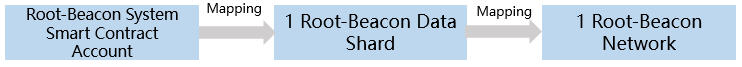
Shard System Smart Contract Account、Normal User Account and Application Smart Contract Account

# Key-pair Generation
# Key-pair of Normal User Account
Private Key
SHA-256 security hashing algorithm is used to generate a random 256-bit private key, starting with "0x".
Example:
0x40fb93846c424a107ac854f52290043e4c57368f035e563f8dc0091be8cc1ff9.
Public Key
Secp256k1 algorithm is used to generate the public key corresponding to the private key.
Example:
0x045f04ab02ef604ee8861b32e5b07ba64070d901daffc5edb0f14a1fc2f27c3b193eff0398023b0ea1285abfd3e1cabc5d83575aa9681880184e8cfd207b02c57f.
Account Address
The ECDSA digital signature algorithm is used to convert the public key into the account address and prefix "T8" according to the account type.
Example:
T800002276a7d58218ac4978733e5cca927a7d86cb7c87.
# Key-pair of Application Smart Contract Account
Key-pair
Application smart contract account uses the same public-private key generation algorithm as normal user account.
Account Address
The application smart contract account address is to add the public key of the contract account and the public key of its parent account bit by bit to obtain a set of array, and then uses ECDSA digital signature algorithm to convert the array into address, and add prefix "T30000".
Example:
T30000Mo9KPHMGZyyn8AwzUJx6dkdZxzUxhgE9hN.
Example of application smart contract account address generation:
std::String xecpubkey_t::to_address(const std::String & parent_addr,const char addr_type,const uint16_t ledger_id)
{
if(parent_addr.empty())
return to_address(addr_type,ledger_id);
uint8_t temp_publickey_data[65];
memcpy(temp_publickey_data, m_publickey_data, sizeof(temp_publickey_data));
const int parent_addr_size = std::min((int)parent_addr.size(),65);
for(int i = 0; i < parent_addr_size; ++i)
{
temp_publickey_data[i] += parent_addr[i];
}
return to_address(temp_publickey_data, addr_type, ledger_id);
}
# Keystore File
# Account Keystore File
The account keystore file is your unique private key and a encrypted file that is used to sign transactions. It allows you to store the key in an encrypted manner.
This approach combines security (an attacker needs the account keystore file and your password to steal your assets) and ease of use (you only need the account keystore file and password to access the assets).
WARNING
If the private key is lost, it means you cant no longer sign the transaction, and your assets are permanently locked up in your account.
So, please keep your private key and account keystore file! Do not disclose your private key and account keystore file password to others!
Keystore file format:
{
"account_address" : "T800002276a7d58218ac4978733e5cca927a7d86cb7c87",
"address" : "2276a7d58218ac4978733e5cca927a7d86cb7c87",
"crypto" : {
"cipher" : "aes-128-ctr",
"cipherparams" : {
"iv" : "09dade6d3ce2741794e49d65f8dd65a4"
},
"ciphertext" : "a45fd491c32ad271039883ed4084e18c57e12cd2c21af1522fe94ba8313634a3",
"kdf" : "scrypt",
"kdfparams" : {
"dklen" : 32,
"n" : 262144,
"p" : 1,
"r" : 8,
"salt" : "9ed2bcb3349392765fec47bb20776cdb69e0e3a4d19d26da65f9371f83cfc2b5"
},
"mac" : "da83cf03746166c877bf319d6371c7f54d518c48c99b1782fdad56e343b812f6"
},
"hint" : "",
"id" : "568498c9-889b-a26d-fa01-bc9a67ffc472",
"key_type" : "owner",
"public_key" : "9b473e552fd05ed2e39d4d3af18367cc98859d50a3eb93805e4706b6b86310c83a2c4e847b662266330cef4cfb7c595ad655ab6a18d86708fe7bc00b589a3a68",
"version" : 3
}
| Parameters | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| account address | Account address. When the key_type is "worker", this is the address of the account that the worker key belongs to. | ||
| address | Ethereum account address. | ||
| crypto | The private key encryption related information. | ||
| cipher | Private key encryption algorithm. | ||
| cipherparams | Cipher encryption algorithm parameters. | ||
| iv | Vector. | ||
| ciphertext | Encrypted private key. | ||
| kdf | Key generation function that lets you encrypt the account keystore file with a password. | ||
| kdfparams | Kdf algorithm parameters. | ||
| dklen | The key length of the private key encryption algorithm. | ||
| n | The number of encryption and decryption operations. The larger the value is, the more the cost of brute force cracking will be, and the the signature speed will be affected as well. | ||
| p | 1 for serial operation, 0 for parallel operation. Serial operations can increase security and also affect the speed of signatures. | ||
| r | Encrypted packet length. | ||
| salt | A randomly generated vector. | ||
| mac | Message authentication code. | ||
| hint | The hint of the password of the account keystore. | ||
| id | uuid. | ||
| key_type | owner key or worker key. | ||
| public_key | Account public key. | ||
| version | Keystore file version. |
# Generate Keystore File
Generate the original private key and perform hexadecimal encoding on the original data.
Generate 32-byte
salt.CryptoPP::AutoSeededRandomPool::GenerateBlockGenerate AES 32-byte encryption key. Where: Kdf algorithm is scrypt, hash algorithm is SHA3-256, with the password, to generate the encryption key.
Generate AES 16-byte
iv.CryptoPP::AutoSeededRandomPool::GenerateBlockGenerate ciphertext. Encryption algorithm is AES128, encryption mode is CTR_Mode.
Calculate 32 byte MAC, the last 16 bytes of aes_key are spliced with the encrypted ciphertext, and then hash (SHA3-256) the spliced data.
Write the above data to the file.
